|
I am a PhD Candidate in Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE) at the University of Texas at Austin, where I am advised by Prof. Aryan Mokhtari and Prof. Sujay Sanghavi. My research focuses on Machine Learning and AI, specifically at the intersection of optimization theory, representation learning, and latent variable models. My work aims to build more efficient and robust large-scale models. My recently accepted paper, Learning Mixtures of Experts with EM: A Mirror Descent Perspective (ICML 2025), demonstrates that the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm can significantly outperform standard optimizers like Adam for training Mixture of Experts (MoE) models. During my research internship at Interdigital, I developed novel solutions for model interoperability by creating a novel framework that allows for explicity distributional enforcement of the aggregate posterior, which resulted in a patent. We additionally submitted our findings as a paper to ICLR 2026 -- Sculpting Latent Spaces with MMD: Disentanglement With Programmable Priors. I earned an MSc in Mathematics & Statistics from McGill university where I was advised by Prof. Tim Hoheisel and Prof. Abbas Khalili and a BSc in Joint Honours Mathematics & Computer Science, also from McGill University. This strong theoretical foundation, combined with hands-on experience from software engineering and data science internships, allows me to bridge the gap between AI theory and real-world application. Contact / Resume / Google Scholar / LinkedIn / GitHub |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NEW
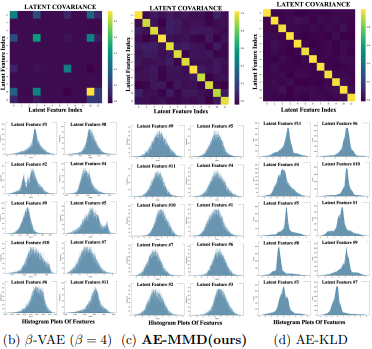
Quentin Fruytier, Akshay Malhotra, Shahab Hamidi-Rad, Aditya Sant, Aryan Mokhtari, and Sujay Sanghavi ArXiv, 2025 Project Page PDF ArXiv We show that the standard KL-based regularizer in VAEs is an unreliable mechanism for learning disentangled representations. Our solution is the Programmable Prior Framework, a novel MMD-based method that explicitly engineers the latent space to achieve state-of-the-art disentanglement without the common reconstruction trade-off. To validate that our method learns mutually independent features, we also introduce the Latent Predictability Score (LPS), a new unsupervised metric for quantifying entanglement on large-scale datasets. |
|
|
|
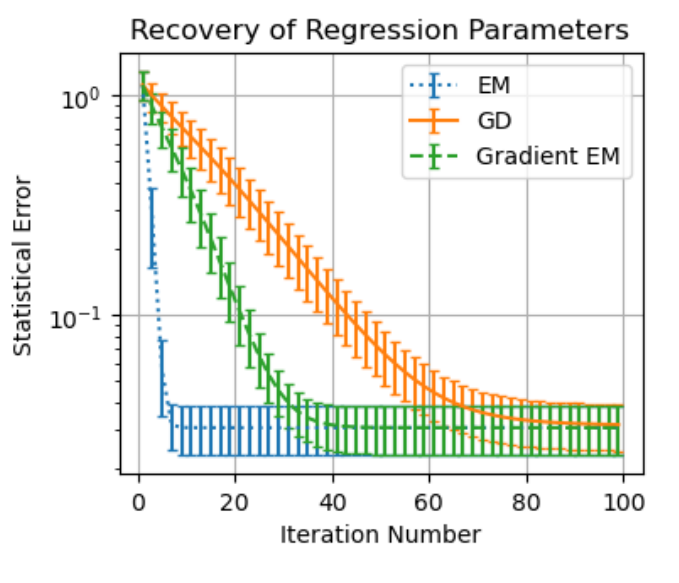
Quentin Fruytier, Aryan Mokhtari, and Sujay Sanghavi ICML 2025 OpenReview PDF ArXiv Slides Poster We provide a theoretical analysis of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm for training Mixture of Experts (MoE) models. Our work connects EM to Mirror Descent to establish new convergence guarantees and shows through theory and experiments that EM can be a faster and more accurate alternative to standard gradient descent. |

|
Quentin Fruytier MSc Thesis, 2023 OpenView This thesis provides a comprehensive review of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm, a powerful tool for parameter estimation in models with latent variables. Spanning from its foundational concepts in the 1970s to its modern applications, this work covers the algorithm's convergence properties and practical uses in mixture models, serving as a valuable resource for researchers. |
|
|

|
Quentin Fruytier This project investigates the failure of traditional rating systems like Elo and Glicko in team-based (n-vs-n) esports. Our simulations reveal a clear and drastic decrease in accuracy as team sizes grow beyond 1v1, highlighting the inability of these algorithms to account for individual performance gaps. We advocate for a novel system that incorporates in-game performance metrics to provide more accurate and responsive player ratings. |

|
Quentin Fruytier PDF Project Page This project analyzes Deep Learning methods for traffic prediction, a key challenge due to complex spatial and temporal patterns. We take a deep dive into the state-of-the-art DCRNN model, investigating how its feature space dimension impacts performance on the METR-LA dataset and proposing specific architectural improvements to enhance prediction accuracy. |
|
|

|
Akshay Malhotra, Quentin Fruytier Los Altos, California, 2025 Patent No. *****, US Patent Application No. 19/337202 The present application patent protects a newly invented framework for deliberate sculpting of the latent space with MMD that achieves learning desired aggregate posterior distributions for the latent space. Targetted applications include Model Interoperability, Quantization, and Performance Monitoring. |
| Website Template |